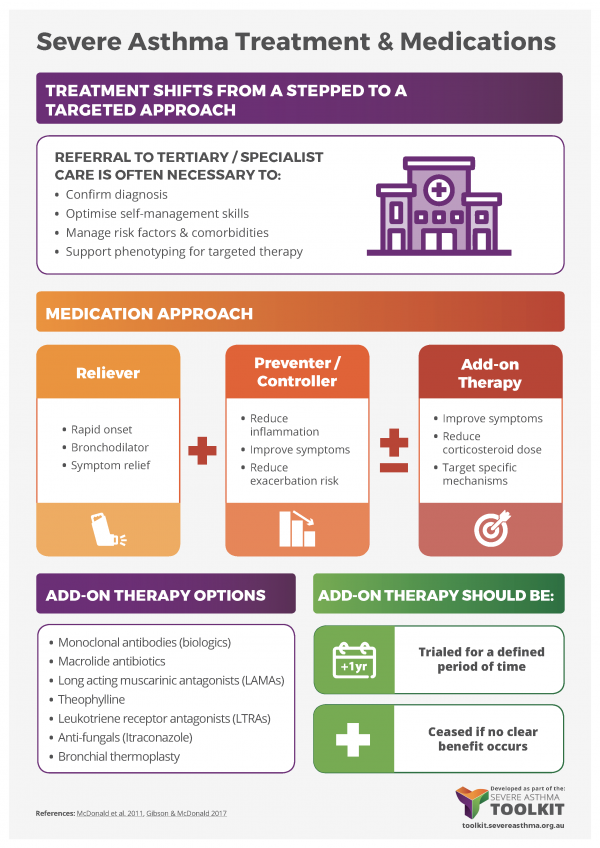
A severe asthma assessment is needed to confirm diagnosis, optimise skills and manage risk factors and comorbidities.
When a diagnosis of severe, treatment refractory asthma has been confirmed, treatment emphasis shifts from a stepped approach to a targeted approach for treatment.
Referral to tertiary care and potentially a severe asthma clinic is often appropriate and necessary, for the integration of add-on therapies into management.
Therapeutic trials of add-on therapies (e.g. tiotropium, anti-fungal agents, montelukast, low dose macrolide antibiotics) may be undertaken for defined periods of time, but clinicians should be prepared to cease these medications if there is no clear sign of benefit. For more information see Add-on Therapies & Monoclonal Antibodies.
Last Updated on