Lung function assessments are critically important to confirm a diagnosis of asthma, to assess for alternative diagnosis and comorbidity and to characterise the degree of functional impairment.

Spirometry
Standard spirometry can provide information about the extent of decreased lung function in patients with asthma (e.g. FEV1, FVC and FEV1/FVC).
Spirometry is essential in the assessment of severe asthma.
- The presence of a large bronchodilator response indicates baseline airflow obstruction and active disease
- Acute bronchodilator responsiveness measured in the lab, clinic or surgery is uncommon
- It has poor sensitivity for asthma
- It is non-specific, and may be present in COPD and bronchiectasis
- When combined with a history that is consistent for asthma, a positive bronchodilator response is strongly supportive of the diagnosis
- Airflow obstruction (i.e. FEV1/FVC ratio < the lower limit of normal) may not be acutely reversible
- Asthma may cause fixed airflow obstruction (James et al. 2005)
- It may however, improve over days, weeks or months with optimal treatment
- The absence of acute bronchodilator responsiveness does not refute the diagnosis of asthma
- FEV1 may vary spontaneously over time in asthma (e.g. due to lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI), exacerbations)
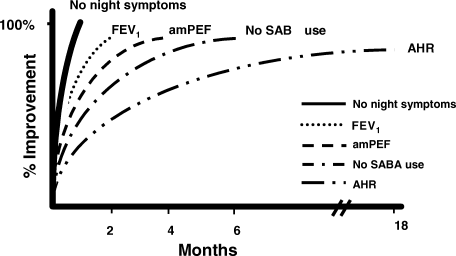
See figure below regarding the time-course of improvement in spirometry asthma following inhaled corticosteroid treatment. Reproduced with permissions from John Wiley and Sons from (Woolcock 2001)
Lung Volumes
Lung volume assessments can complement spirometry findings and can identify potential issues such as air trapping and/or hyperinflation.
- Lung size (Total Lung Capacity – TLC) measured by body plethysmography, should be measured at least once in asthmatic subjects, which will rule out restriction. An FVC ≥ about 90% of predicted will effectively rule restriction out.
- The subdivisions of lung volume may be useful since gas trapping (increased RV/TLC) ratio and hyperinflation (increased FRC/TLC ratio) may be present and indicates persisting airflow obstruction, even when spirometry is normal.

Lung Diffusing Capacity for Carbon Monoxide (DLCO)
Measurement of gas transfer in the lung can identify abnormalities. Low results are indicative of significant emphysema or lung fibrosis. Results should be normal or increased in patients with severe asthma. This measurement has little use in asthma, including severe asthma.
Airway Hyperresponsiveness (AHR)
Airway hyperresponsiveness is a hallmark of asthma.
- It is non-specific
- Its absence does not exclude asthma, and may indicate;
- Episodic asthma
- Well-controlled asthma
- Its presence, in conjunction with a compatible history is strongly supportive of an asthma diagnosis
- Discordance, i.e. a history suggestive of uncontrolled asthma but no AHR, should make the clinician question the diagnosis
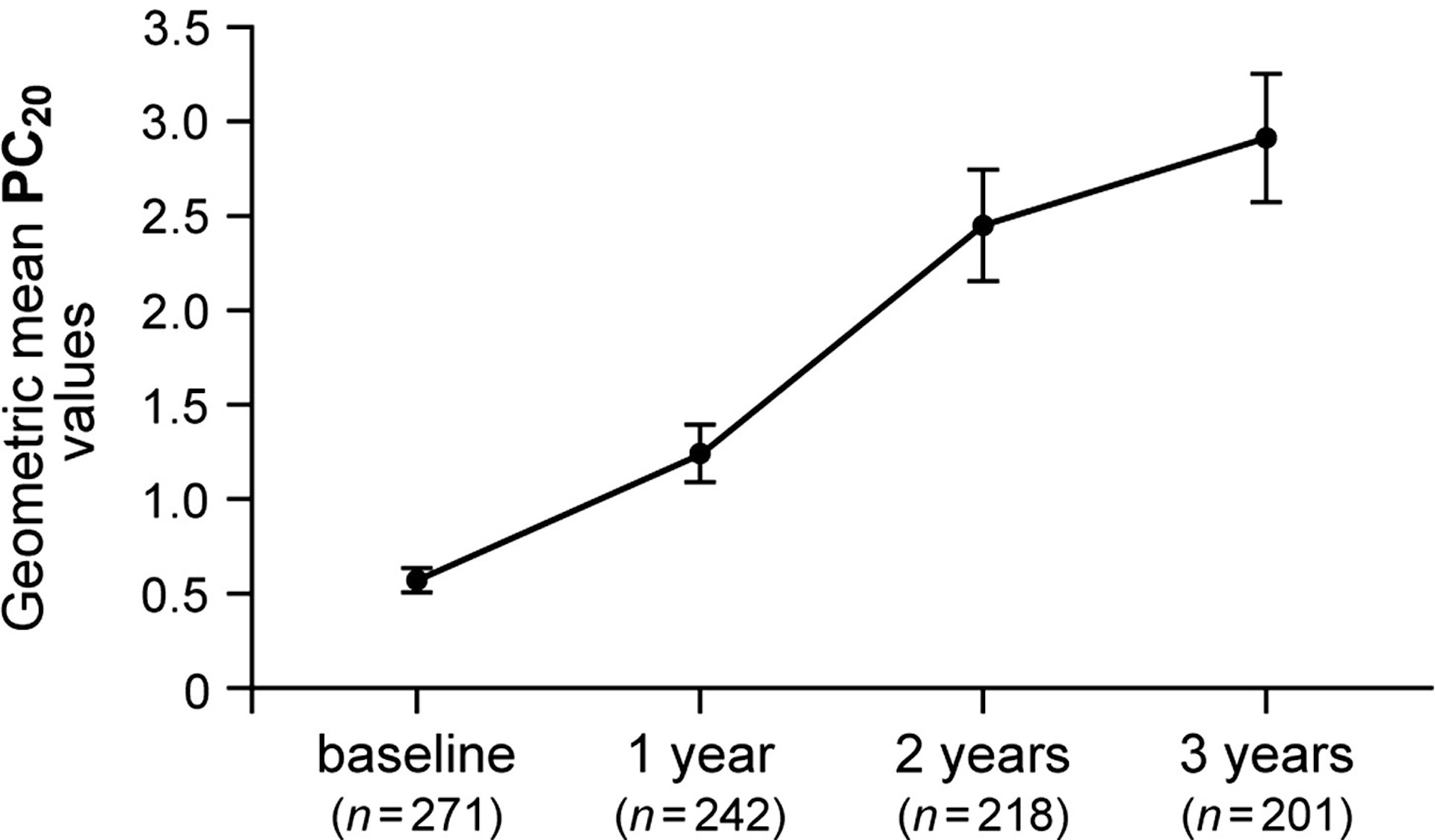
- AHR improves slowly over time with treatment (see example below). Therefore, the absence of AHR may be consistent with well-treated asthma.
Bronchial Provocation Testing (BPT)
There are a number of BPTs available:
- Mannitol (Aridol)
- Methacholine
- Eucapnic voluntary hyperpnoea (EVH)
- Hypertonic saline
- Exercise
Notes:
- Cardiopulmonary exercise testing often does not elicit bronchoconstriction in exercise-induced asthma, due to the ambient conditions being unfavourable to inducing bronchoconstriction (use EVH instead)
- Mannitol challenge tests are readily available across Australia and NZ
- Methacholine challenge is also available in some labs as an alternative, direct challenge test.
- Some patients with severe asthma cannot undergo BPT due to low baseline FEV1 (<60% of predicted precludes BPT) or inability to withhold short-acting bronchodilators for ≥6 hours.
- The absence of AHR should alert the clinician to re-assess the diagnosis of asthma (when the patient is not receiving any ICS), or the diagnosis of severe asthma.
Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT)
FOT is used to measure respiratory system impedance during tidal breathing (and other specialised breathing manoeuvres). It is a tidal breathing measurement of respiratory system (upper and lower airways, lung and chest wall) impedance. Impedance describes the ‘impediment’ to flow generation from any given pressure applied at the airway opening. Therefore, higher impedance results in less flow for a given driving pressure. A simple description of FOT is available in (King 2011)
At the present time, the following commercial devices are available in Australia:
There are published normal predicted equations available (Oostveen et al. 2013), but no substantial values are available for Australia using currently commercial devices. The recent normal predicted values are published for Australia, with measurements made using a generic device (Brown et al. 2010).
Clinic use of FOT:
- Potential applications in severe asthma will likely appear in clinical practice within the next few years. These will need to be supported by clinical research studies and increased knowledge around the measurement.
- An ATS/ERS Technical Standards Document will be published in 2018 that will contain a clinically relevant review of methods and scenarios for clinical application of FOT.
Potential clinical uses include:
- Use as an alternative to spirometry for bronchial provocation challenge
- Measuring changes in lung function between clinic visits – this may complement or be an alternative to spirometry in those unable or unwilling to have spirometry,
- Detection of vocal cord dysfunction (Ioan et al. 2016)
- Monitoring in the home, as an alternative to spirometry.
Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF)

PEF monitoring for severe asthma:
- May be particularly useful in severe asthma, compared with the general asthmatic population
- May be useful to confirm the presence of uncontrolled asthma
- There may be significant disparity between symptoms and PEF variability; the clinical significance should be carefully evaluated for each individual
- Minimal variability suggests that asthma is well controlled – it may be due to symptom ‘hyperperception’ or incorrect diagnosis
- Conversely, a high degree of variability may be present with few symptoms – this indicates a ‘poor perceiver’, which may require a different management strategy
- ‘Personal Best’ (recorded from 2-3 weeks of daily recordings) or ‘average’ may be used
- The time course over which improvement occurs in severe asthma is not known.
- There are no clearly defined methods or strong recommendations for developing a peak flow-based action plans. However;
- They should be individualised
- There is a need for clinical studies on efficacy and design of written asthma plans (both peak flow and symptom based)
- For more information see Management – Asthma Education – Self-Monitoring
For user-friendly information and instructions on PEF use for asthma monitoring, see:
Last Updated on
